NSF Certification for Supplements: Complete Analysis of Third-Party Testing Standards
The NSF certification mark appears quietly on supplement labels, often overshadowed by bold marketing claims and colorful packaging. Yet for those who understand its implications, this modest three-letter emblem represents one of the most meaningful forms of quality assurance available in the largely self-regulated supplement industry 1U.S. Food and Drug Administration. “Dietary Supplements: What You Need to Know.” FDA Consumer Health Information, 2022..
NSF International certification provides independent verification of supplement quality through laboratory testing, facility audits, and ongoing monitoring protocols that exceed FDA requirements. Unlike pharmaceutical drugs, dietary supplements do not require pre-market safety or efficacy approval, creating an environment where contaminated, mislabeled, or adulterated products regularly reach consumers 2Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, Public Law 103-417, 103rd Congress..
This comprehensive analysis examines NSF’s certification methodologies, testing protocols, and verification standards. The evidence reveals how NSF’s systematic approach addresses critical gaps in supplement quality control while providing consumers, healthcare professionals, and athletes with reliable tools for product evaluation and risk assessment.
Origins and Evolution of NSF International
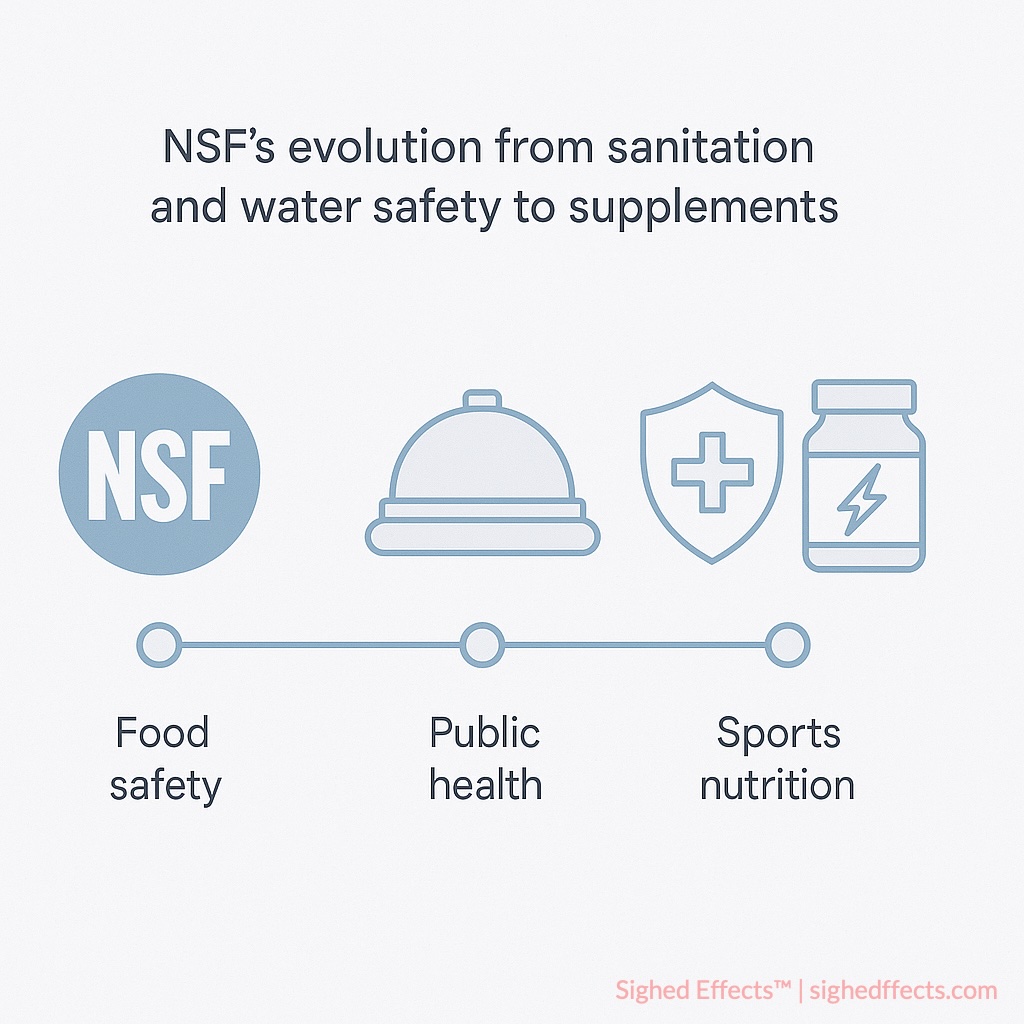
NSF International emerged from the National Sanitation Foundation, established in 1944 to address public health challenges in food safety and sanitation during the post-war industrial expansion 3NSF International. “History and Mission: 75 Years of Public Health Protection.” Organizational Documentation, 2019.. The organization’s initial mandate focused on developing unified public health codes for foodservice environments, addressing contamination risks that were poorly understood and inconsistently regulated.
Over subsequent decades, NSF expanded its scope to encompass water treatment systems, food equipment, plumbing infrastructure, and building materials—all areas where invisible quality failures could have far-reaching public health consequences. The organization’s approach emphasized scientific rigor over commercial interests, establishing NSF as an independent nonprofit entity rather than a government agency or for-profit testing company.
Entry into Supplement Verification
NSF’s expansion into dietary supplement certification occurred during the explosive growth period following passage of the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) in 1994 4Cohen, P.A. “American roulette—contaminated dietary supplements.” New England Journal of Medicine, 2009; 361(16): 1523-1525.. As supplement popularity increased while regulatory oversight remained minimal, NSF identified a critical need for independent quality verification in this expanding market.
The organization’s existing expertise in analytical chemistry, toxicology, and industrial safety positioned it uniquely to address supplement quality challenges. NSF laboratories already possessed the equipment and methodological knowledge necessary for high-precision contaminant detection and ingredient verification. This technical infrastructure enabled NSF to develop comprehensive supplement certification programs that went beyond simple batch testing to include manufacturing facility audits and ongoing quality monitoring.
Global Expansion and Recognition
NSF International currently operates in over 180 countries and maintains ISO-accredited laboratories worldwide 5NSF International. “Global Operations and Accreditation Status.” Annual Report, 2023.. The organization participates in developing more than 90 public health standards across multiple industries while maintaining its core mission of independent verification and public health protection.
In the supplement industry, NSF functions as an independent referee, systematically confirming that labeled ingredients match actual product contents while screening for contaminants that could compromise safety or legal compliance. This role requires NSF to maintain strict independence from commercial interests while developing testing methodologies that can detect increasingly sophisticated adulteration techniques.

NSF Certification Methodologies and Testing Protocols
NSF’s approach to supplement certification employs multiple verification layers designed to address different aspects of product quality and safety. The organization offers several certification tiers, each tailored to specific user needs and risk tolerances while maintaining consistent standards for analytical rigor and documentation transparency.
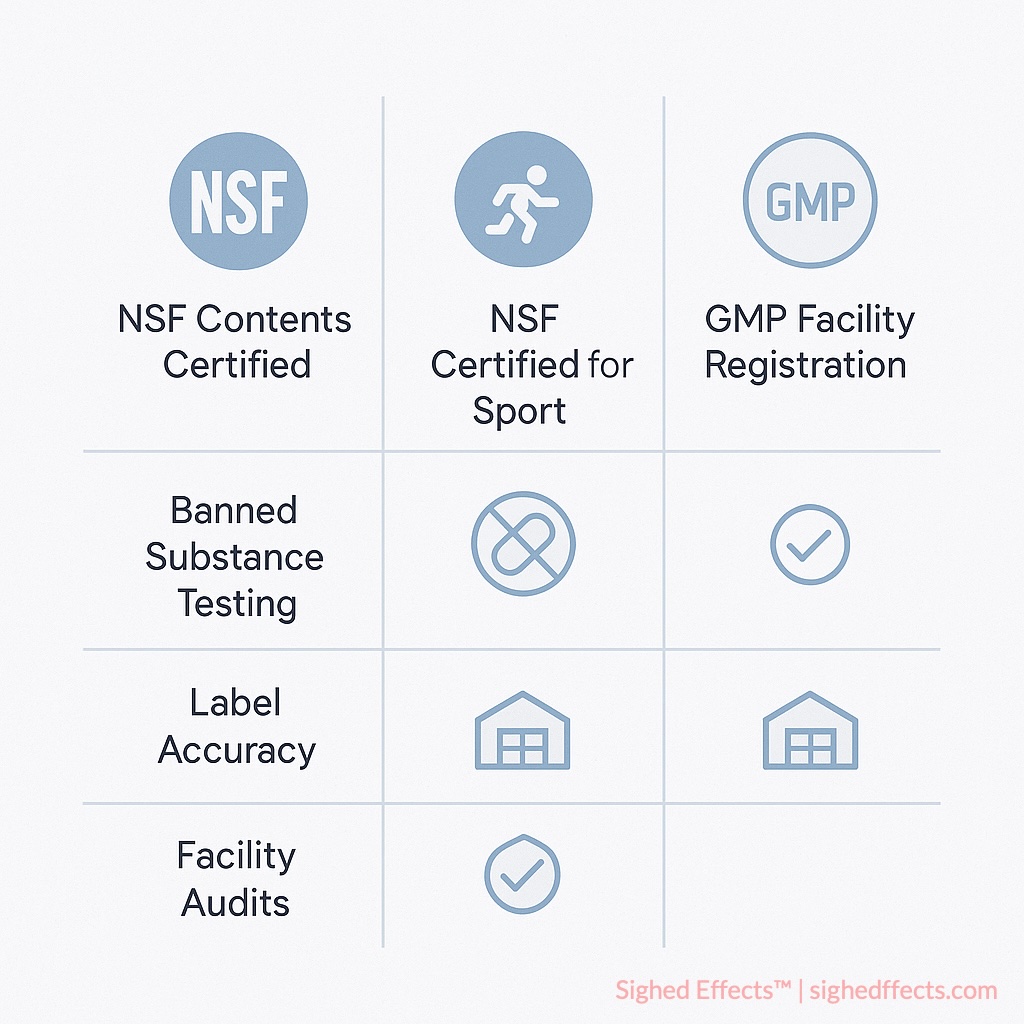
NSF Contents Certified (Standard Certification)
NSF Contents Certified represents the foundational level of NSF verification, providing comprehensive quality assurance for general supplement use. This certification requires products to undergo laboratory testing and facility auditing across multiple parameters:
Ingredient Identity and Potency Verification
- Chemical analysis confirms labeled compounds match actual contents
- Quantitative testing verifies ingredient concentrations within specified tolerances
- Botanical supplements undergo species authentication through DNA analysis
- Stability testing ensures consistent potency throughout product shelf life
Contaminant Screening and Safety Testing
- Heavy metals analysis (lead, mercury, cadmium, arsenic) using ICP-MS methodology
- Microbiological testing for pathogenic bacteria, yeast, and mold contamination
- Pesticide residue screening for botanical ingredients and agricultural inputs
- Residual solvent testing to detect manufacturing process contaminants
Manufacturing Quality Assurance
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) facility audits ensure FDA compliance
- Supply chain documentation verifies ingredient sourcing and traceability
- Quality control system evaluation confirms consistent production standards
- Documentation review validates batch records and testing procedures
NSF Certified for Sport: Elite Athletic Protection

NSF Certified for Sport extends beyond standard certification to address the specialized needs of competitive athletes and organizations subject to anti-doping regulations. This program screens for over 280 substances prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) and major sports leagues 6NSF International. “NSF Certified for Sport Program Standards.” Athletic Supplement Testing Protocols, 2023..
Banned Substance Screening
- Comprehensive testing for WADA Prohibited List compounds
- Detection of anabolic agents, stimulants, hormone modulators, and diuretics
- Screening for masking agents and substances with similar chemical structures
- Analysis of emerging designer drugs and synthetic analogs
Batch-Level Testing Requirements
- Individual lot testing before product release to market
- Ongoing shelf audit sampling from retail locations
- Post-certification monitoring through unannounced facility inspections
- Adverse event tracking and response protocols
Label and Claims Verification
- Marketing materials reviewed for anti-doping compliance
- Health claims evaluated against regulatory standards
- Ingredient disclosure requirements exceed standard labeling laws
- Batch number traceability systems for contamination investigation
Facility Auditing and Manufacturing Oversight

NSF certification requires comprehensive evaluation of manufacturing facilities beyond standard GMP inspections. These audits examine operational systems, quality control procedures, and environmental conditions that could affect product integrity:
Physical Infrastructure Assessment
- Cross-contamination prevention systems and equipment design
- Raw material storage conditions and inventory management protocols
- Environmental monitoring for temperature, humidity, and air quality
- Waste management and cleaning validation procedures
Personnel and Training Evaluation
- Staff training documentation and competency assessment
- Standard operating procedure (SOP) implementation and compliance
- Quality assurance team qualifications and oversight responsibilities
- Corrective action protocols for non-conformance events
Documentation and Traceability Systems
- Batch record accuracy and retention requirements
- Supplier qualification and ongoing monitoring programs
- Certificate of analysis verification and third-party testing coordination
- Product recall procedures and consumer notification systems
Scientific Basis for NSF Testing Standards
The analytical methodologies employed by NSF certification programs reflect current best practices in pharmaceutical and food safety testing, adapted specifically for dietary supplement applications. These methods undergo regular validation and updates to address emerging contaminants and evolving regulatory requirements.
Analytical Chemistry and Detection Limits
NSF laboratories utilize advanced analytical instrumentation including liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) for compound identification and quantification 7Association of Official Analytical Chemists. “Guidelines for Single Laboratory Validation of Chemical Methods.” AOAC Guidelines, 2022.. These techniques enable detection of contaminants at parts-per-billion levels, providing sensitivity sufficient to identify trace contamination that could affect athletic drug testing results.
Method Validation and Quality Control
- Reference standard materials ensure accurate quantification across analytical runs
- Blank sample analysis confirms absence of laboratory contamination
- Duplicate sample testing verifies measurement precision and reproducibility
- Proficiency testing through inter-laboratory comparison programs
Detection Limit Optimization
- Banned substance detection thresholds align with WADA technical requirements
- Heavy metal limits reflect current toxicological safety data
- Microbial testing employs culture-based and molecular detection methods
- Statistical analysis confirms measurement uncertainty and confidence intervals
Contamination Risk Assessment
NSF’s systematic approach to contamination detection addresses multiple pathways through which prohibited substances or harmful compounds can enter supplement products:
Raw Material Contamination
- Supplier auditing and ingredient source verification
- Certificate of analysis review and independent confirmation testing
- Cross-contamination assessment during ingredient processing and storage
- Agricultural pesticide and herbicide residue monitoring
Manufacturing Process Contamination
- Shared equipment evaluation for cross-product contamination risk
- Cleaning validation protocols and residue detection methods
- Environmental monitoring for airborne and surface contamination
- Personnel hygiene and protective equipment compliance assessment
Post-Manufacturing Contamination
- Packaging material testing for migration of harmful compounds
- Storage condition monitoring during distribution and retail phases
- Shelf-life stability studies under accelerated aging conditions
- Retail sampling programs for post-market surveillance
Comparative Analysis: NSF vs Alternative Certification Programs
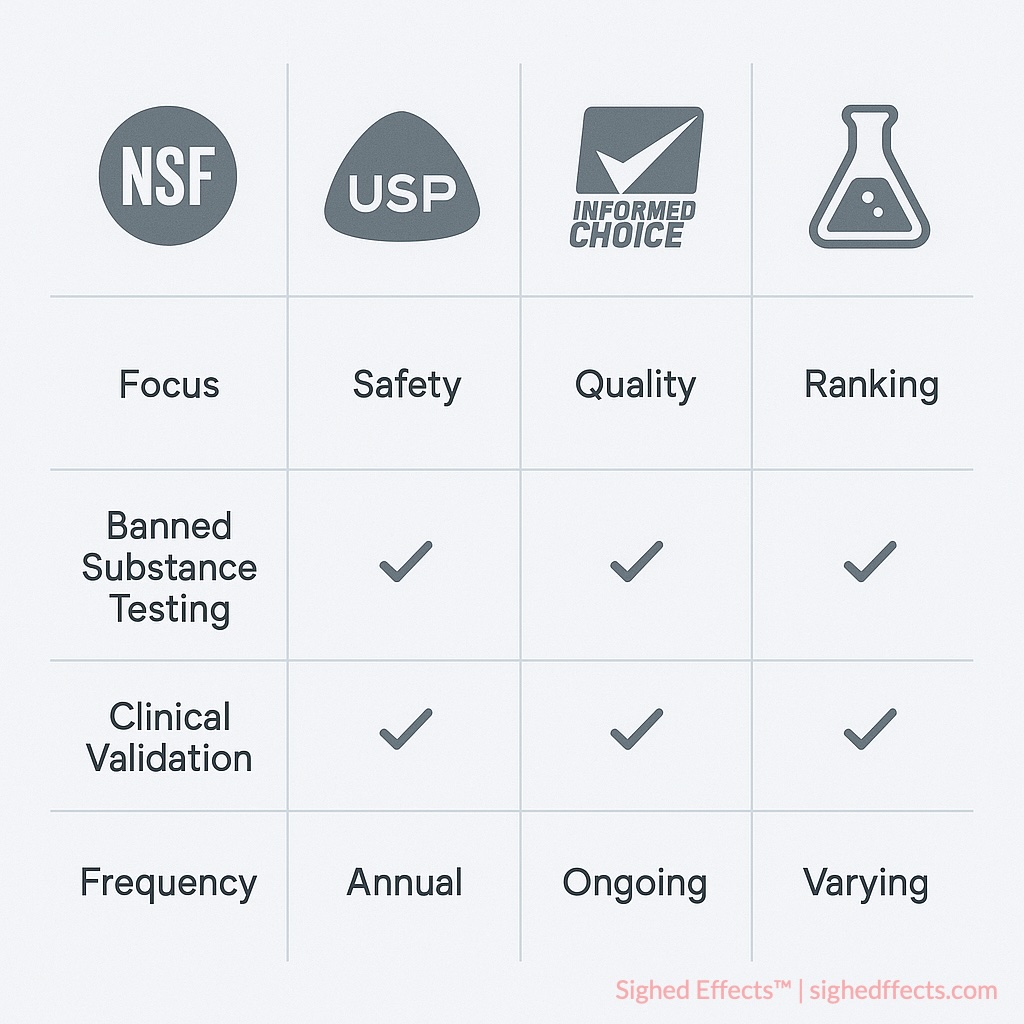
The supplement certification landscape includes multiple organizations offering verification services, each with distinct methodologies, testing scope, and credibility levels. Understanding these differences enables informed decision-making about product selection and risk assessment.
NSF vs USP Verified Supplements
USP Verified certification focuses primarily on pharmaceutical-grade quality standards, emphasizing ingredient identity, potency accuracy, and dissolution testing for tablet and capsule formulations 8United States Pharmacopeia. “USP Verified Dietary Supplements Program.” Quality Standards Documentation, 2023.. While USP provides excellent verification of basic quality parameters, it does not include banned substance screening or athlete-specific compliance testing.
NSF Certified for Sport incorporates USP-level quality verification while adding comprehensive anti-doping protection through prohibited substance screening and batch-level monitoring. This makes NSF the preferred choice for athletic environments where banned substance exposure could result in career-ending consequences.
Regulatory Recognition Comparison
- USP standards referenced in FDA regulations and pharmacopoeial monographs
- NSF Certified for Sport recognized by USADA, NCAA, and professional sports leagues
- Both organizations maintain ISO accreditation and participate in international standards development
- Neither certification guarantees clinical efficacy or therapeutic outcomes
NSF vs Informed Choice Certification
Informed Choice operates as a global banned substance testing program administered by LGC Group, emphasizing monthly batch testing and international sports recognition 9LGC Group. “Informed Choice Global Anti-Doping Certification.” Testing Standards, 2023.. The program provides WADA-compliant screening with particular strength in European and international markets.
Key Differences in Approach
- NSF requires lot-by-lot testing before product release; Informed Choice emphasizes periodic monitoring
- NSF includes comprehensive label accuracy verification; Informed Choice focuses primarily on banned substances
- NSF maintains publicly searchable databases with batch-specific information
- Informed Choice offers broader international recognition in global markets
Selection Criteria for Users
- Choose NSF for comprehensive quality verification plus banned substance protection
- Choose Informed Choice for international distribution or European market focus
- Both provide adequate anti-doping protection for competitive athletes
- NSF offers superior transparency through public database access
Independent Laboratory Testing Alternatives
Some supplement companies employ independent laboratories for product testing without formal certification program participation. These arrangements may provide valuable quality data but lack the systematic oversight and ongoing monitoring that characterize formal certification programs.
Limitations of Ad Hoc Testing
- No standardized testing protocols or detection limit requirements
- Limited facility auditing or manufacturing process evaluation
- Potential conflicts of interest when manufacturers select testing laboratories
- Absence of ongoing monitoring or post-market surveillance programs
Advantages of Formal Certification Programs
- Standardized methodologies ensure consistent testing across products and brands
- Independent oversight reduces conflicts of interest and selection bias
- Ongoing monitoring provides continuous quality assurance
- Public databases enable consumer verification of certification claims
Economic and Market Implications of NSF Certification
The decision to pursue NSF certification involves significant financial and operational commitments that affect product pricing, market positioning, and competitive dynamics within the supplement industry.
Certification Costs and Market Positioning
Direct Certification Expenses
- Initial application and documentation review fees
- Laboratory testing costs for comprehensive analytical panels
- Facility audit expenses and potential corrective action requirements
- Ongoing monitoring fees and batch-level testing charges
Indirect Operational Costs
- Manufacturing process modifications to meet certification standards
- Enhanced documentation and quality control system implementation
- Supply chain transparency requirements and supplier qualification programs
- Marketing and educational initiatives to communicate certification value
Market Premium and Consumer Response
- Certified products typically command 15-30% price premiums over non-certified alternatives
- Healthcare professionals show preference for certified products in clinical recommendations
- Athletic organizations increasingly mandate certified products for team use
- Consumer awareness of certification benefits remains limited but growing
Competitive Advantages and Market Differentiation
Brand Credibility and Trust Building
- NSF certification signals commitment to quality over marketing hype
- Third-party verification reduces consumer uncertainty and purchase hesitation
- Professional endorsements and institutional adoption enhance brand reputation
- Certification requirements filter out competitors unwilling to meet transparency standards
Risk Management and Liability Protection
- Independent verification reduces legal exposure for contamination incidents
- Documentation trails support product liability defense strategies
- Quality assurance systems prevent costly recalls and regulatory enforcement actions
- Professional indemnity considerations favor certified products in clinical settings
Market Access and Distribution Opportunities
- Military and government contracts increasingly specify certified product requirements
- Professional sports organizations limit approved products to certified brands
- Healthcare systems develop preferred vendor relationships with certified manufacturers
- International export markets may require or prefer third-party certification
Clinical and Professional Applications
NSF certification serves distinct functions across different user populations, from elite athletes to healthcare practitioners to general consumers seeking quality assurance in supplement selection.
Athletic and Anti-Doping Applications

Professional Sports Integration Major professional sports leagues including the NFL, MLB, NHL, and NBA recognize NSF Certified for Sport as an acceptable risk mitigation strategy for supplement use 10World Anti-Doping Agency. “Supplement Use Guidelines for Athletes.” WADA Educational Resources, 2022.. Team nutritionists and medical staff frequently restrict approved supplement lists to certified products to protect athlete eligibility and organizational reputation.
Collegiate Athletic Programs
- NCAA compliance officers recommend certified products to reduce inadvertent doping violations
- Scholarship eligibility protection motivates widespread adoption among student-athletes
- Educational programs emphasize certification as essential component of safe supplementation
- Institutional liability concerns drive policy preferences for verified products
Olympic and International Competition
- USADA explicitly recognizes NSF Certified for Sport in athlete education materials
- International federations increasingly adopt similar verification requirements
- Anti-doping laboratories coordinate with certification programs for contamination investigation
- Elite training centers stock exclusively certified products to eliminate risk exposure
Healthcare and Clinical Settings
Physician and Healthcare Provider Preferences Healthcare practitioners face increasing pressure to provide evidence-based supplement recommendations while managing liability concerns related to product quality and safety 11MacLellan, J. et al. “Physician attitudes toward dietary supplement regulation and clinical recommendations.” Journal of the American Medical Association, 2022; 327(8): 742-750.. NSF certification provides a systematic approach to quality verification that supports clinical decision-making.
Institutional Healthcare Applications
- Hospital systems develop formularies that prioritize certified supplement products
- Outpatient clinics recommend certified brands to reduce patient safety concerns
- Integrative medicine practitioners use certification status as selection criteria
- Patient education materials emphasize importance of third-party verification
Clinical Research and Academic Medicine
- Research studies increasingly specify certified products to ensure intervention consistency
- Academic medical centers prefer certified supplements for clinical protocol development
- Grant funding agencies may require certified products for supplement intervention studies
- Publication standards evolve to include product verification as methodological requirement
Consumer Education and Market Awareness
Public Understanding of Certification Benefits Consumer awareness of supplement certification remains limited despite growing recognition of quality problems in the industry. Educational initiatives by healthcare organizations, athletic associations, and consumer advocacy groups increasingly emphasize third-party verification as essential component of safe supplementation practices.
Information Access and Verification Tools
- NSF maintains public databases enabling product certification verification
- Batch-specific information allows consumers to confirm individual product testing
- Educational materials explain certification processes and quality implications
- Mobile applications facilitate real-time certification status checking
Regulatory Environment and Policy Implications
NSF certification operates within the broader regulatory framework governing dietary supplements, complementing rather than replacing FDA oversight while providing additional quality assurance mechanisms.
FDA Relationship and Regulatory Recognition
The FDA references NSF certification standards in warning letters to supplement companies, demonstrating regulatory recognition of certification program value 12U.S. Food and Drug Administration. “Warning Letter to Supplement Manufacturer: Adulterated Products.” FDA Enforcement Actions, 2023.. This regulatory acknowledgment enhances certification credibility and supports industry adoption of third-party verification practices.
Regulatory Enforcement Applications
- FDA investigators cite lack of third-party testing in enforcement actions
- Import inspections may consider certification status in risk assessment
- Adverse event investigations examine product certification and quality history
- Congressional hearings reference certification programs in policy discussions
International Regulatory Harmonization
- Global regulatory agencies increasingly recognize NSF certification standards
- International trade agreements may incorporate third-party verification requirements
- Export markets demonstrate preference for certified products
- Regulatory convergence supports standardized quality expectations
Future Policy Development
Legislative and Regulatory Trends Ongoing policy discussions in Congress and FDA focus on enhanced supplement quality standards and potential mandatory certification requirements. NSF’s established infrastructure and methodological expertise position the organization to support expanded regulatory oversight while maintaining industry flexibility and innovation capacity.
Industry Self-Regulation Evolution
- Trade associations increasingly promote voluntary certification adoption
- Industry best practice guidelines reference third-party verification standards
- Market pressures drive competitive certification among leading brands
- Consumer advocacy organizations support mandatory certification policies
Risk Assessment and Safety Considerations
NSF certification addresses multiple categories of supplement-related risks, from acute contamination hazards to long-term quality consistency concerns.
Contamination Risk Mitigation

Heavy Metal Exposure Prevention Recent studies demonstrate significant heavy metal contamination in unverified supplement products, with lead, mercury, cadmium, and arsenic detected at levels exceeding safety thresholds 13Klenow, S. et al. “Heavy metal contamination in protein supplements: market analysis and health risk assessment.” Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2022; 159: 112789.. NSF testing protocols establish detection limits well below regulatory action levels, providing protection against chronic exposure risks.
Banned Substance Contamination
- Cross-contamination during manufacturing can introduce prohibited substances at detectable levels
- Raw material adulteration may occur without manufacturer knowledge or intent
- Batch-to-batch variability requires ongoing monitoring rather than single-point testing
- International ingredient sourcing increases contamination risk exposure
Microbiological Safety Assurance
- Pathogenic bacteria contamination can cause serious illness, particularly in immunocompromised individuals
- Yeast and mold contamination may trigger allergic reactions or respiratory symptoms
- Manufacturing environment monitoring prevents systematic contamination issues
- Storage and distribution condition requirements maintain product safety throughout supply chain
Long-Term Quality Consistency
Stability and Potency Maintenance NSF certification requirements include stability testing to ensure maintained potency throughout product shelf life. This testing identifies degradation pathways and storage condition requirements that preserve ingredient effectiveness and prevent formation of harmful degradation products.
Batch-to-Batch Variability Control
- Consistent manufacturing processes reduce potency variation between production runs
- Quality control testing identifies and corrects systematic production problems
- Statistical process control methods monitor manufacturing performance trends
- Corrective action procedures address non-conformance events before distribution
Implementation Guidelines and Best Practices
Effective utilization of NSF certification requires understanding of program limitations, appropriate product selection criteria, and integration with broader health and safety practices.
Product Selection Strategies
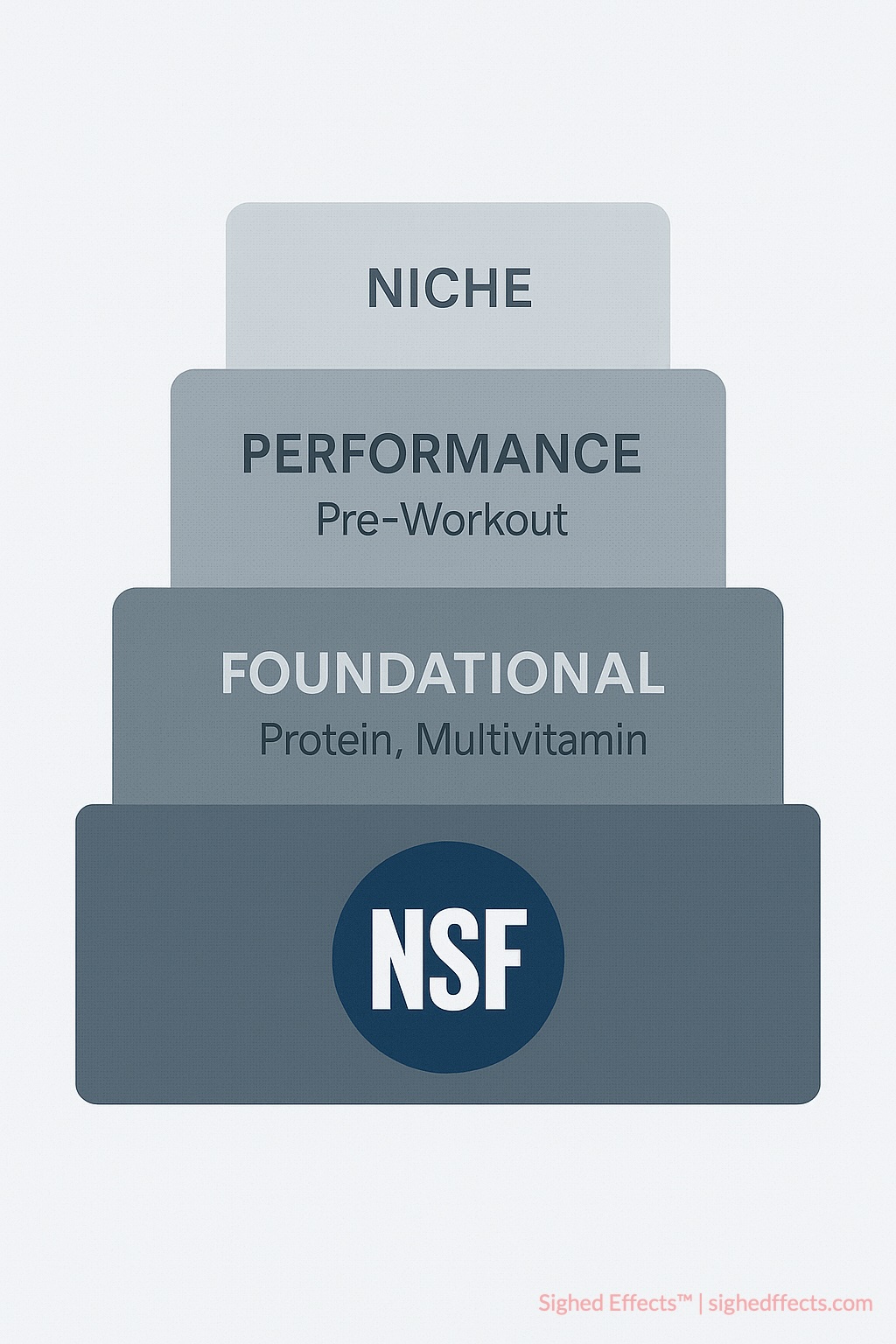
Foundation Supplement Prioritization Focus NSF certification requirements on daily-use supplements that create highest exposure levels over time. These foundational products—including multivitamins, protein powders, creatine, and omega-3 supplements—benefit most from rigorous quality verification and contamination screening.
Athletic and Professional Application Guidelines
- Individuals subject to drug testing should exclusively use Certified for Sport products
- High-stakes professional environments require maximum contamination protection
- Team nutritionists and medical staff should establish certified-product-only policies
- Educational programs must emphasize certification verification procedures
Healthcare Provider Recommendations
- Clinical practitioners should prioritize certified products in patient recommendations
- Institutional formularies should preferentially include verified supplement options
- Patient education materials should explain certification benefits and verification methods
- Liability considerations support preference for independently tested products
Verification and Authentication Procedures

Database Utilization
- Always verify certification claims through official NSF databases
- Check batch-specific information when available for individual products
- Confirm certification expiration dates and renewal status
- Report suspected certification fraud to NSF and regulatory authorities
Ongoing Monitoring Practices
- Periodically recheck certification status for regularly used products
- Monitor recall notices and safety alerts from certification organizations
- Stay informed about certification program updates and standard revisions
- Maintain documentation of certification verification for professional accountability
Limitations and Areas for Improvement
While NSF certification provides valuable quality assurance, the system has inherent limitations that users must understand for appropriate risk assessment and product selection.
Scope and Coverage Limitations
Market Penetration and Accessibility NSF certification covers only a small fraction of available supplement products, limiting consumer access to verified options across all product categories. Cost and complexity barriers prevent many smaller manufacturers from pursuing certification, potentially creating market concentration among larger brands.
Ingredient and Category Coverage
- Novel ingredients may lack established testing protocols or safety data
- Emerging product categories may not fit existing certification frameworks
- Custom formulations and personalized supplements challenge standardized verification approaches
- International ingredient sourcing complicates traceability and verification requirements
Efficacy and Therapeutic Value Assessment NSF certification verifies safety and quality but does not evaluate clinical effectiveness or therapeutic value. Consumers must separately assess scientific evidence supporting ingredient efficacy and appropriate dosing for intended applications.
Technical and Methodological Considerations
Detection Limit and Analytical Sensitivity While NSF testing methods achieve high analytical sensitivity, detection limits may not identify contamination below threshold levels. Emerging contaminants and novel synthetic compounds may escape detection until analytical methods undergo updating and validation.
Temporal and Batch Variability
- Single-point testing cannot identify intermittent contamination events
- Manufacturing changes between certification periods may affect product quality
- Supply chain disruptions can introduce new contamination sources
- Seasonal variation in raw materials may influence product consistency
Economic Analysis and Market Dynamics
The financial implications of NSF certification extend beyond direct certification costs to encompass broader market positioning, competitive dynamics, and consumer value propositions.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Manufacturers
Investment Requirements and Return Considerations Manufacturers pursuing NSF certification must invest in enhanced quality systems, documentation procedures, and ongoing testing programs. These investments typically require 12-18 months to implement fully and may necessitate changes to established manufacturing partnerships and supply chain relationships 14Nutrition Business Journal. “Third-Party Testing and Certification Market Analysis.” Industry Report, 2022..
Revenue Impact and Market Premium
- Certified products command average price premiums of 20-35% over non-certified alternatives
- Professional and institutional sales channels show strong preference for certified products
- Brand reputation and consumer trust benefits extend beyond individual product sales
- Reduced liability exposure and recall risk provide long-term financial protection
Competitive Positioning and Market Differentiation NSF certification creates competitive barriers that filter market participants based on commitment to quality and transparency. This filtering effect can benefit certified brands through reduced competition while potentially limiting market entry for innovative smaller companies.
Consumer Economic Considerations
Value Proposition Assessment Consumers must evaluate whether certification premium pricing aligns with individual risk tolerance, intended use patterns, and quality priorities. For general health maintenance applications, certification may provide limited tangible benefits compared to careful brand selection and product research.
Risk-Adjusted Pricing Analysis
- High-risk applications (athletic drug testing, clinical conditions) justify certification premium
- Daily-use supplements benefit more from certification than occasional-use products
- Professional liability and career consequences support premium pricing for at-risk populations
- Insurance and healthcare cost offsets may partially justify certification expenses
Future Directions and Industry Evolution
The supplement certification landscape continues evolving in response to regulatory developments, technological advances, and changing consumer expectations for product quality and transparency.
Technological Integration and Innovation
Advanced Analytical Techniques Emerging analytical technologies including blockchain traceability systems, real-time contamination monitoring, and artificial intelligence-powered quality prediction models offer potential enhancements to traditional certification approaches 15Blockchain in Healthcare Consortium. “Supply Chain Transparency and Product Authentication.” Technology Assessment Report, 2023..
Digital Verification and Consumer Access
- Mobile applications for real-time certification verification and batch tracking
- QR code integration enabling instant access to product testing data
- Consumer notification systems for recalls and safety alerts
- Integration with electronic health records for clinical decision support
Predictive Quality Assessment Machine learning algorithms analyzing manufacturing data, environmental conditions, and historical contamination patterns may enable predictive quality assessment that identifies risks before contamination events occur.
Regulatory Evolution and Policy Development
Potential Mandatory Certification Requirements Congressional discussions regarding enhanced supplement oversight may result in mandatory third-party testing requirements for specific product categories or risk levels. NSF’s established infrastructure positions the organization to support expanded regulatory requirements while maintaining operational efficiency.
International Harmonization Initiatives
- Global recognition agreements between certification organizations
- Standardized testing protocols across international markets
- Mutual recognition of certification standards for international trade
- Coordinated contamination investigation and response procedures
Market Expansion and Access Improvement
Cost Reduction and Efficiency Enhancement Technological advances and economies of scale may reduce certification costs over time, improving access for smaller manufacturers and expanding certified product availability across price points and market segments.
Educational Initiative Expansion
- Healthcare provider training programs on certification evaluation and utilization
- Consumer education campaigns highlighting quality differences and risk factors
- Athletic organization partnerships for comprehensive supplementation safety programs
- Academic research collaboration to quantify certification benefits and outcomes
Conclusion
NSF certification represents a systematic approach to supplement quality assurance that addresses critical gaps in the current regulatory framework. Through comprehensive laboratory testing, facility auditing, and ongoing monitoring protocols, NSF provides independently verified quality assurance that exceeds FDA requirements and supports informed decision-making across diverse user populations.
The evidence demonstrates that NSF Certified for Sport offers the most rigorous verification available for supplements used in athletic and professional environments where contamination risks carry severe consequences. For general consumers, NSF Contents Certified provides valuable quality assurance that may justify premium pricing based on individual risk tolerance and quality priorities.
However, certification limitations must be acknowledged. NSF verification covers only product safety and quality parameters, not clinical efficacy or therapeutic value. Market penetration remains limited, and certification costs may restrict access for some manufacturers and consumers. These limitations require balanced consideration in product selection and risk assessment processes.
As the supplement industry continues expanding while regulatory oversight remains limited, third-party certification programs like NSF serve essential functions in protecting consumer safety and supporting informed supplement use. The systematic approach to quality verification, transparency requirements, and ongoing monitoring protocols distinguish legitimate certification from marketing claims while providing practical tools for navigating an increasingly complex marketplace.
For individuals and organizations seeking to optimize supplement safety and quality outcomes, NSF certification provides a valuable filter that reduces uncertainty while enabling focus on efficacy research and appropriate clinical application rather than basic quality concerns.

